MS SQL Server: Query performance¶
Table of contents
Introduction¶
Sometimes queries can become slow due to large data volumes or levels of nesting. This page explains how to identify the query performance, and how queries can be optimized.
Analysing query performance¶
Let’s say we want to analyse the following query:
query {
authors(where: {name: {_eq: "Mario"}}) {
rating
}
}
In order to analyse the performance of a query, you can click on the Analyze button on the Hasura console:

The following query execution plan is generated:

We can see that a sequential scan is conducted on the authors table. This means that MS SQL Server goes through every row of the authors table in order to check if the author’s name equals “Mario”.
The cost of a query is an arbitrary number generated by MS SQL Server and is to be interpreted as a measure of comparison rather than an absolute measure of something.
Read more about query performance analysis in the MS SQL Server explain statement docs.
Query optimization¶
Using MS SQL indexes¶
MS SQL Server indexes are special lookup tables that MS SQL Server can use to speed up data lookup. An index acts as a pointer to data in a table, and it works very similar to an index in the back of a book. If you look in the index first, you’ll find the data much quicker than searching the whole book (or - in this case - database).
Let’s say we know that authors table is frequently queried by name:
query {
authors(where: {name: {_eq: "Mario"}}) {
rating
}
}
We’ve seen in the above example that by default MS SQL Server conducts a sequential scan i.e. going through all the rows. Whenever there is a sequential scan, it can be optimized by adding an index.
The following statement sets an index on name in the authors table.
CREATE INDEX ON authors (name);
Data -> SQL tab in the Hasura console.Create a migration manually and add your create index statement to the up.sql file.
Also, add an SQL statement to revert that statement to the down.sql file in case you need to roll back the migration.
Apply the migration by running:
hasura migrate apply
You can add an index by making an API call to the schema_run_sql metadata API:
POST /v2/query HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
X-Hasura-Role: admin
{
"type": "run_sql",
"args": {
"source": "<db-name>",
"sql": "<create index statement>"
}
}
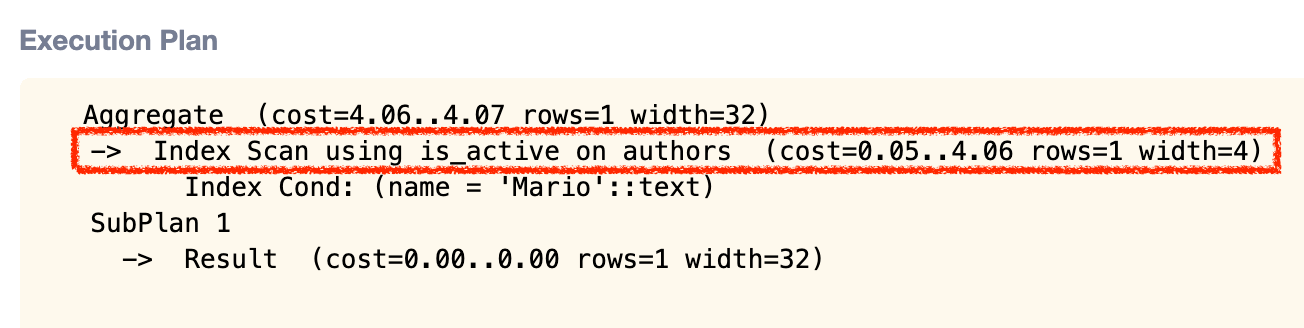
Let’s compare the performance analysis to the one before adding the index.
What was a sequential scan in the example earlier is now an index scan. Index scans are usually more performant than sequential scans.
We can also see that the cost of the query is now lower than the one before we added the index.
Note
In some cases sequential scans can still be faster than index scans, e.g. if the result returns a high percentage of the rows in the table. MS SQL Server comes up with multiple query plans and takes the call on what kind of scan would be faster.
